Specifics - IBR analysis:
IBR stands for Invalid but Resident. It is part of the new storage concept that replaces XSTORE (expanded storage) for
handling memory activity as of z/VM 6.3. It contains several frame/page lists.
When the system needs real storage (memory), the algorithm selects frames/pages from the user and system owned lists.
These pages are put in IBR state. Any access to a page in IBR state by guests results in revalidation. Otherwise,
the frame associated with an IBR page is added to the global aging list to be reused.
Linux servers tend to do polling which causes the server to look at data then go back to sleep. If the few pages it
touches at each dispatch get paged out (moved to DASD), the system page rate goes up. A high page rate will cause system
performance impacts. (See Storage Analysis for more details.)
There are settings that can be changed to improve IBR performance, see below for recommendations.
ESAUSTR - User Storage Utilization - Shows virtual and resident storage/paging rates activity. Both screen and report samples:
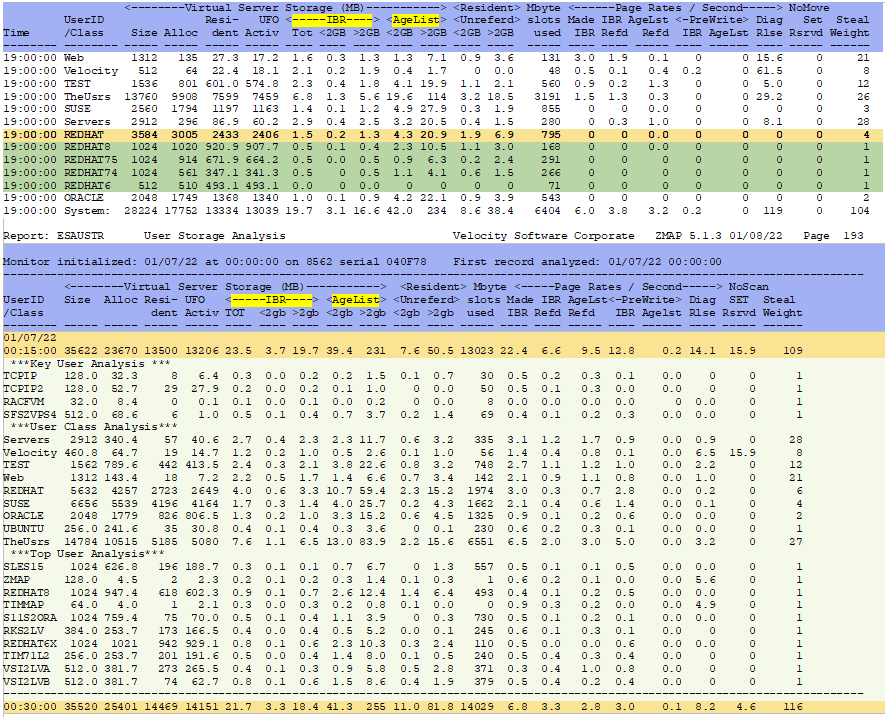
The following settings are suggested by Velocity Software:
- Use Q AGELIST to view the current settings.
- Update Target size to 5.0% - SET AGELIST SIZE 5.0% - if needed. This gives a bigger buffer area. (The default is 2%)
- Update Early writes to yes - SET AGELIST EARLYW YES - if needed. This allows unused pages to be written out early. (The default is YES) This may not be necessary if using Solid State DASD for paging devices.
- Update Keep slot to yes - SET AGELIST KEEPS YES - if needed. This keeps the storage address longer. (The default is YES) This may not be necessary if using Solid State DASD for paging devices.
- This can be done in one command if preferred - SET AGELIST SIZE 5% EARLYWRITES YES KEEPSLOT YES
- Use the ESAUSTR screen/report to verify changes - review the IBR TOT column. Number going up is goodness. This shows there are more pages still resident so are more easily accessed if needed.
Back to top of page
Back to Flow Chart main page

